Practices to reduce IT operating costs: This blog post shows how a company can reduce the costs of its IT operations and improve the efficiency of IT resources by optimizing its main infrastructure and adopting the best practices in the operations of servers. The practices described are effective to reduce operating costs and free up resources (human and financial) they offer and add value to the company and its customers.
Introduction
Even in the best of times, IT managers face multiple challenges; providing excellent services 24×7 with a limited budget makes things a little bit difficult to manage. Studies by different analysts indicate that about 80% of the company’s IT budget is usually devoted to operations and maintenance. This leaves only 20% for IT innovation which is yet one factor increasing the values of the companies. In these uncertain economic times, with tight budgets, this ratio may change in favor of the operations and maintenance, which reduces the share for the improvement of services for the companies.
Microsoft solutions can help data center managers to improve the effectiveness of the main infrastructure of the organization, thus it can free human and financial resources for new IT innovations.
Infrastructure Optimization
Working with Microsoft and its partners, organizations can better plan and execute their investments, get the ability to define the appropriate level of server optimization, and reduce the costs of server operations. To facilitate their task, Microsoft has developed the optimal model of core infrastructure. With this model, the company can learn from its current position in terms of IT efficiency and can determine how to improve and how optimize its IT infrastructure.
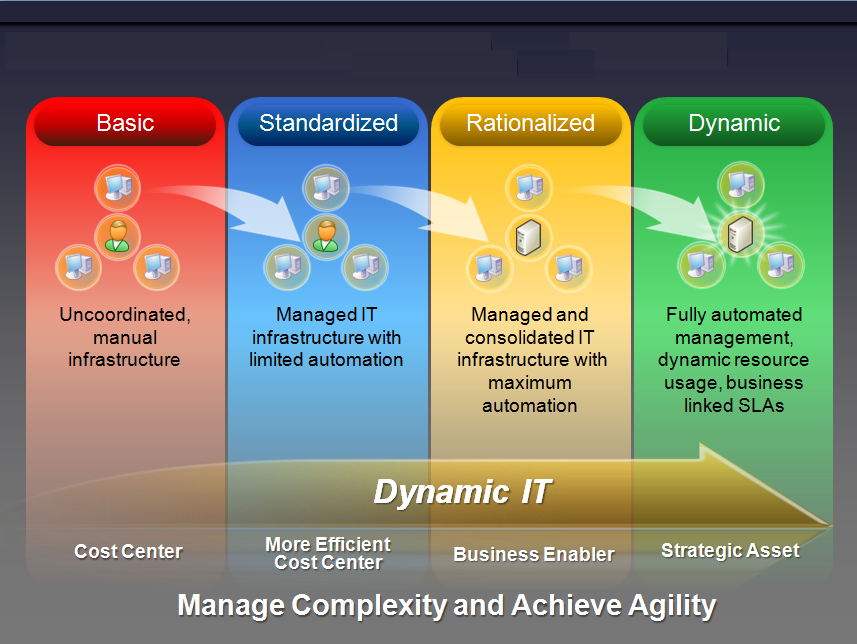
Optimization model of the main infrastructure
Microsoft has developed this model to define the level of efficiency so IT organizations can achieve the goals of better management of their IT infrastructure. Four levels of operational efficiency have been identified: basic, standardized, rationalized, and dynamic. These four levels correspond to the technological capabilities and describe the effectiveness of services in specific scenarios. Processing from one level to another, the company can gain efficiency and reduce operating costs and maintenance.
To better evaluate the level of optimization of the existing infrastructure and categorize areas for improvement, the infrastructure optimization model covers different areas: identity management and access rights, administration of workstations, servers, and devices, network security, protection and data recovery, and security administration. This post focuses on practices in each of these sectors to identify and measure their impact on system availability and operating costs in different scenarios servers.
Recommended Practices for Core Infrastructure
The identification and adoption of best practices for optimizing infrastructure means reducing operating costs, and improving IT service levels and agility. Studies have shown that there is a close relationship between the adoption of recommended practices and benefits. For example, these practices reduce the number of calls to the support of users and therefore reduce the cost per user. This post describes a relationship less well-known, which is between the adoption of best practices for servers and resulting benefits (improved system availability and lower costs) in the main scenarios of servers.
Server infrastructure scenarios
The study focuses on six scenarios essential to business operations:
- Collaboration
- Data Management
- Identity and Access
- Connectivity
- Printing
These scenarios are analyzed from the point of view of the optimization of the main infrastructure; practices analyzed in this study corresponded to the administration and operation of each server scenario, not activities related to the specific scenario. Although the practices described below are common to three or more scenarios, they induce different effects on personnel costs and the availability of the architecture in the scenario studied.
Collaboration:
The collaboration scenario includes practices in the administration of enterprise and Web content, research and document storage, document workflows, social networks, and monitoring projects.
Collaboration: Benefits of Core Infrastructure Optimization
Companies manage collaboration servers for streamlined optimization to avoid those disadvantages that occur at the basic level. By automating the management of clustered servers and other routine tasks, modernized organizations have reduced costs and time spent by the server.
Management tools of core infrastructure based on rules for protective maintenance and standardized practices to improve systems availability in enterprises at a standardized level. Companies have efficient tools for further reducing the impact of system downtime by automatically deploying patches and operating server clusters with fail-over and automatic recovery.
Collaboration: Best Practices
In this scenario, the application of best practices has greatly reduced the cost of computer operation. Collaboration is a server scenario among the most recent. Nevertheless, companies see the benefits of adopting recommended practices in this area and adopt them quickly.
The practical impact: 47% of participants in the survey that use clustered servers spend less than $24,000 in IT costs through servers. Much of this difference is due to the efficiency gains achieved in the management of database collaboration within this deployment model. Recommended practices for the commissioning, patching, and deployment of machines have also been the source of significant savings in the cost of IT labor.
Practices widely adopted: The use of alert thresholds for the basic performance parameters, regular maintenance of the operating system, and the use of standardized images have reduced the cost of IT labor in the range of 15,000 to 18,000 dollars per server. These practices improve efficiency through automation, monitoring, and rule-based standardized maintenance practices.
The practices adopted less often: Five practices (integration of automated management of incidents, integration with databases, predictive maintenance, automatic integration in systems management, automated deployment, and integration to store metadata and identification centralized) are rarely adopted. However, the adoption of these practices leads to lower costs.
IT labor from 11,000 to $17,000 per server. These practices reflect the capacity of automatic tracking systems, deployment, and incident response identifying the major problems and the main causes, with minimal intervention from the IT department.
Data Management:
The scenario includes data management practices that affect server file shares and databases in the infrastructure.
Data Management: Benefits of Core Infrastructure Optimization
In a company where the infrastructure optimization level is reached for streamlined data management servers, operating costs fall by 63% per server and each administrator manages about 3 times more servers over firms located at basic. Automated processes of Virtualization deployment and simplify server security contribute to the work of staff in a reduction of costs and improved performance time server.
The availability of data in companies that are at a standardized level of optimization is greater than the availability in companies located at the basic level. On the other hand, data availability with streamlined business was slightly lower than with Standardized business. This difference is because the practices of the Rationalized level are implemented for other objectives such as profitability or agility.
Data Management: Best Practices
In this scenario, you will find two trends: the clear advantage that represents Virtualization systems management data, and the low rate of adoption of automated management practices despite their advantages.
Practical Impact: Server Virtualization enables organizations to reduce their fleet equipment, surfaces, and premises costs of system administration. These savings reach $2,300 per server per year in labor costs for computer companies adopting the practices of Virtualization. Automation also plays an important role. By adopting the creation, conversion, and management of virtual servers, it becomes possible to allocate resources dynamically, which improves the utilization of materials, reduces the number of systems, and reduces power consumption and other costs.
Practices widely adopted: In this scenario, according to participants in this study, two widely adopted practices brought value. Standardizing the process of adding, moving, or changing data management servers can ensure that only proven and effective procedures are used to perform these routine tasks. This practice, which helps IT departments to eliminate repetitive tasks and downtime, reduced 1,400 dollars per year costs of IT labor. Thresholds basic parameters, a practice performance monitoring based on rules, reduced from 700 dollars per server annual cost of IT labor.
The practices adopted less often: Only 17% of study participants have implemented automated management systems and database-driven predictive maintenance. They obtained a reduction in labor costs of $1,100 computers per server per year compared to other companies. The savings are based on the application of rules and predefined actions triggered by system events monitoring tools and automated management.
Identity and Access
Identity and access incorporate practices that apply in the administration server identities and access rights. Access management and identity include support for LDAP servers.
Identity and Access: Benefits of Core Infrastructure Optimization
In this scenario, organizations practicing streamlined operations show significant differences in terms of labor costs per user per computer server.
Server availability is almost the same levels between standardized and streamlined. Indeed, in this scenario, improvements in availability are mostly due to the combination of more efficient processes, and tools. The features that support these practices reduce the downtime of servers when administrators engage in troubleshooting, change materials, and provide network maintenance.
Identity and access: Best Practices
After installation, the servers managing identities and access rights require relatively little maintenance and management. Therefore, the operating costs are low and the impact of the implementation of best practices is limited. However, some features such as authentication, automated commissioning, or integration into central store metadata identities constitute recommended practices of infrastructure optimization. As a result, the adoption of best practices for this scenario has a positive effect on other scenarios.
Practical impact: Clustering of servers provides redundancy and recovery that reduce the risk of stopping server identities and access rights. Features such as automatic commissioning reduce response time and IT staff.
Practices widely adopted: Four practices widely adopted (failover servers standardization, new images of the operating system, standardization of images, and maintenance of operating systems) simplify routine tasks. These practices reduce the number of different configurations to manage. They reduce the cost of IT labor by 140 to $200 per server.
The practices adopted less often: Practices and automated deployment of automatic management of incidents contribute to cost savings, but their adoption rate remains low (below 30%). These practices reduce the workload and costs of staff by providing automatic responses upon detection of problems. They are also able to automate deployments using scripts thoroughly tested.
This scenario includes the practices required to manage server software for email and to ensure the quality and responsiveness of email services.